Purpose
Observe the olecranon from the side.
Check the Radiocapitellar line, Anterior humeral line, fat pad sign .
To correctly assess the fat pad, bend the elbow to exactly 90 degrees. If not, the fat pad is pushed upward and appears to be a lesion.
Prior confirmation
Measure the size of the “carry angle” (5 – 15 degree) from the image obtained by AP projection.
Positioning
Seat the patient in the chair.
Raise the upper arm, elbow joint, and wrist joint to shoulder height.
Bend the elbows at right angles.
tilt the wrist 10 degrees (carry angle) from horizontal.
If the patient is in bad condition, you should irradiate X-rays horizontally.
CR, distance, field size
CR : capitulum humeri
Distance : 100cm
Field size : Includes the half of humerus and forearm.
Exposure condition
50kV / 4mAs
Grid ( – )
Image, check-point
Normal (Radiopaedia)
Abnormal (dislocation) (Radiopaedia)
Abnormal (Radial head fracture) (Radiopaedia)
Medial and lateral epicondyles overlap.
Videos
Related materials
Fat pad sign suggests a fracture.
The following video is recommended to learn about fat pad sign.
anterior fat pad sign (+) : Intra-articular fracture is suspected due to the presence of joint effusion.
posterior fat pad sign (+) : Intra-articular fracture is strongly suspected because it represents a large accumulation of joint fluid. Fatty layer not normally observable.
fat pad sign (-) : It is not evidence of a fracture.
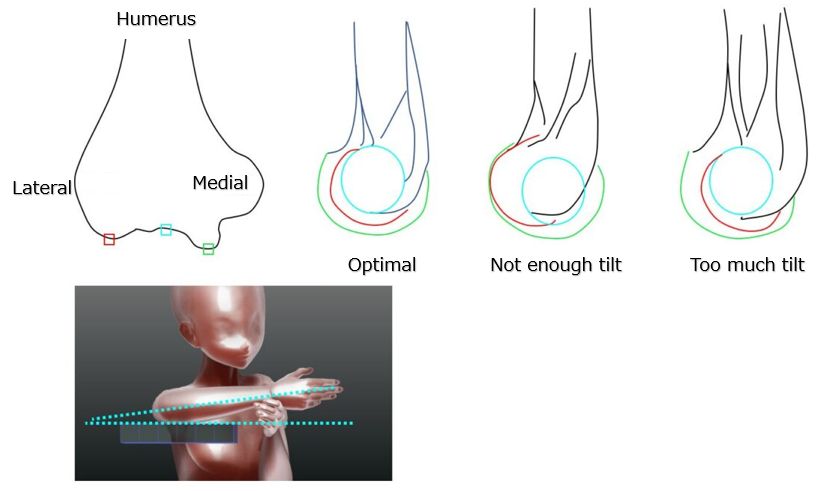
Three edges can be observed in concentric circles. ( Fig.6-3 )
If the radius overlaps the humerus, the wrist is over raised.
If the radius is away from the humerus, the wrist is not raised enough.
Determinants of radial head fracture
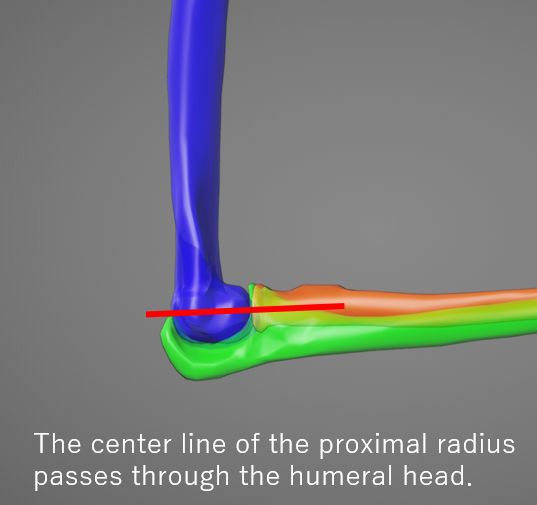
The center line of the proximal radius passes through the humeral head. If this line deviates from the humeral head, it presents a radial head dislocation.(Radiocapitellar line)
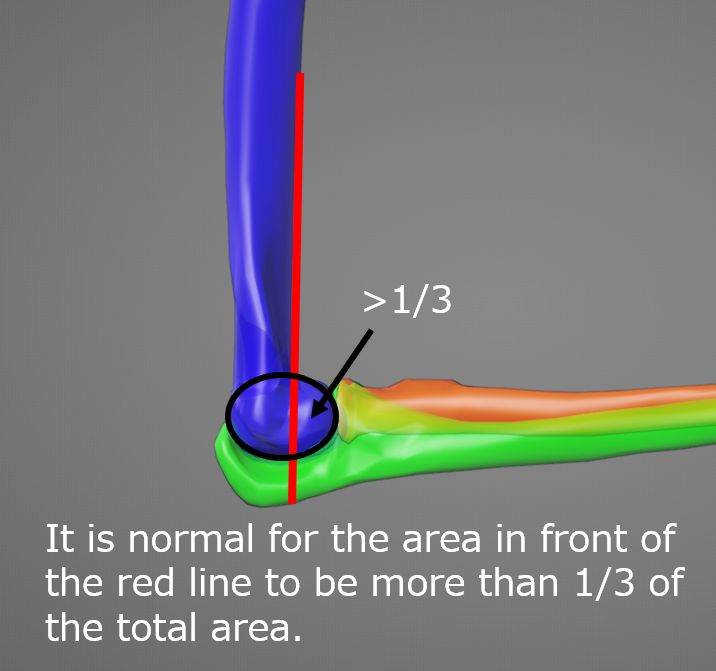
Determinants of supracondylar fracture
More than 1/3 of the humeral head should be present anteriorly to the line drawn along the anterior humeral margin. Otherwise, a supracondylar fracture with posterior dislocation of the distal fragment is suggested. When a fracture is evident, the anterior humeral line can help assess the degree of posterior dislocation. (Anterior humeral line) (Anterior humeral line)