Purpose
A variation of the Ducroquet profile view.
Diagnosis of Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI).
Measurement of the alpha angle.
Detection of non-sphericity in the femoral head-neck junction.
Suitable for observing the femoral head and neck.
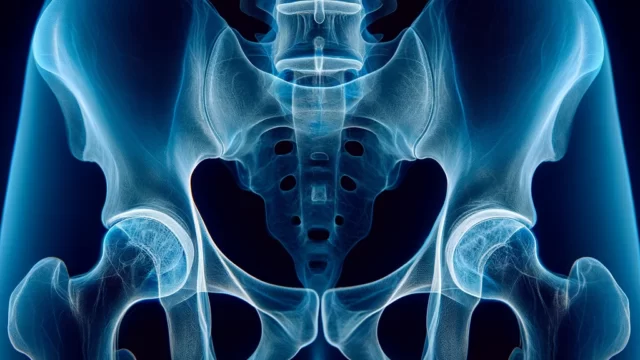
Observation of the relationship between the femoral head and the acetabulum.
Prior confirmation
Confirm whether to take the image in 90° flexion or 45° flexion.
Remove any obstacles.
Positioning
Supine or standing position.
Flex the hip joint of the examined side at 90° or 45°.
Keep the lower leg of the examined side parallel to the bed.
Abduct the lower leg of the examined side by 20°.
Use positioning blocks to prevent body movement.
Align the sagittal plane and cassette center axis.
Align the X-ray center with the cassette center.
CR, distance, field size
CR : Direct the X-ray vertically towards the midpoint between the Anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) of the examined side and the symphysis pubis (center of the groin crease).
Distance : 100cm.
Field size : Include from the proximal 1/3 of the thigh to the midline, and from the ASIS to the buttock skin surface vertically.
Exposure condition
75kV / 25mAs
Grid ( + )
Suspend respiration
Image, check-point
Normal (Radiopaedia)
Fig.5
Dunn view (90 degree)
Dunn view (45 degree)
The femoral head, neck, greater trochanter, and acetabulum should be clearly visualized.
The alpha angle should be measurable. (Normal alpha angle is 50° or less)
There should be no motion blur due to movement.
Videos
Related materials
Radiographic Evaluation of the Hip